Four Essential Steps for Successful Non-Destructive Test
Method Validation
by Alec Alpert
⇓ Download this article as PDF
The test method validation (TMV) process usually starts with determining which test methods on a project need validation and which do not. Test methods needing validation are validated to confirm their fit and suitability for the intended purpose, performance to an acceptable level, and reliability over time. In other words, validation must demonstrate that the precision and accuracy limits are met with regard to diverse appraisers (technicians, operators), various production batches, and variable test equipment. There are basically four types of TMV:
1. Variable/Non-Destructive
2. Variable/Destructive
3. Attribute/Non-Destructive
4. Attribute/Destructive Table
In this article, I address the first type: Variable/Non-Destructive TMV. Typically, the objective of TMV is to ensure that the measurement system (MS) is suitable for its intended purpose and capable of consistently providing valid measurements. From my experience, the most efficient approach to measurement system assessment (MSA) is to follow the four steps described below.
Step 1: Prepare the TMV Protocol
The TMV protocol is a formal document that spells out how the MSA will be accomplished. Although every company has its own procedures and templates for TMVs, a basic TMV protocol includes the following items:
• Cover page with document title, document number, document version, and project number
• Purpose
• Scope
• Applicable documents
• Responsibilities
• Definitions
• Test method description
• Sample size justification
• Test/measurement procedure
• Data collection methodology
• Acceptance criteria for the gage R&R
The key items in the TMV protocol are:
• Test/Measurement Procedure. This describes detailed test/measurement steps, test and measuring equipment, appraisers’ qualifications, training, units or batches to be tested or measured, data-collection methodology, etc. In other words, it covers in detail all of the logistics of the MSA.
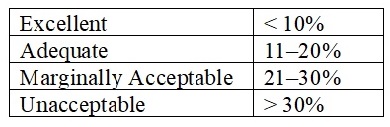
• Acceptance Criteria. The test/measurement data are analyzed using the gage-R&R methodology. The industry’s typical gage-R&R assessment of the measurement variation as a percentage of precision to tolerance (% P/T) is graded as follows:
Step 2: Execute the TMV Protocol
Execution of the TMV protocol boils down to implementing the test/measurement procedure and analyzing the raw measurement data collected by appraisers, as follows:
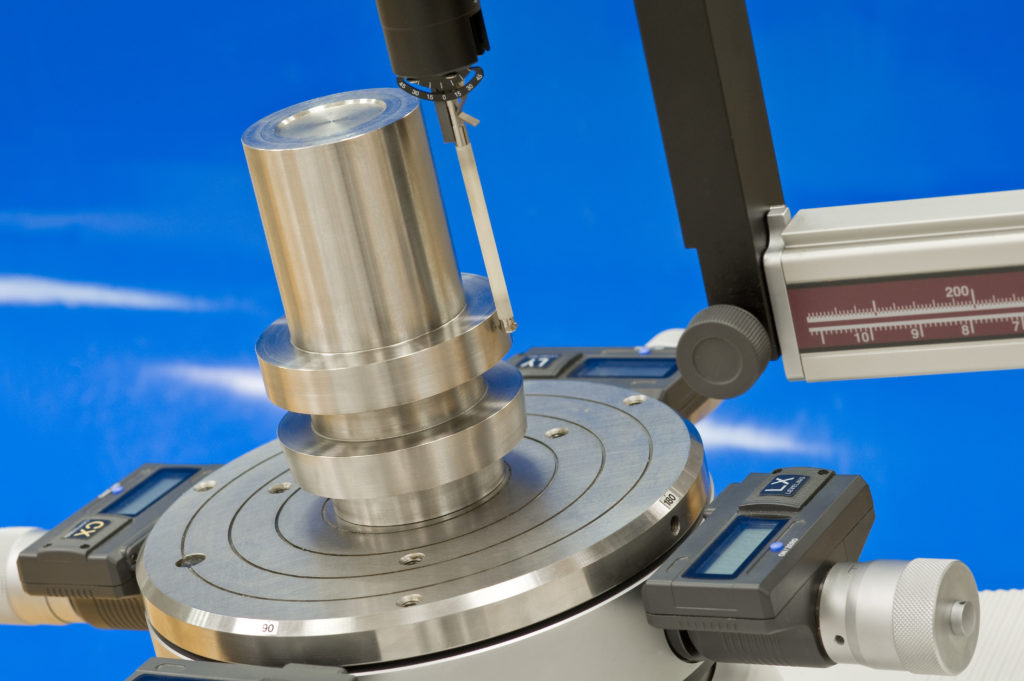
• Test Equipment. Equipment used for the TMV must be assessed to ensure its qualification and calibration. All validation testing must be done on qualified, calibrated equipment. Equipment qualification is therefore a prerequisite of TMV.
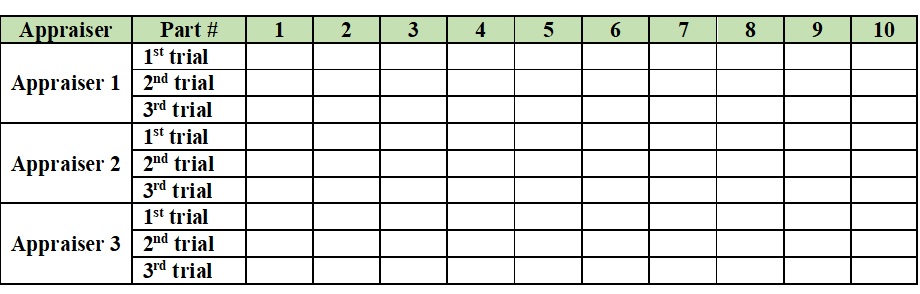
• Data-Collection Methodology. Typically, a minimum of three appraisers take measurements on a sample of 10 parts, three times, each collecting 30 measurements. This results in 90 measurements in total between the three appraisers. Hence, the data-collection table looks like this:
• Sample Randomization. When assigning parts to appraisers in the data-collection step, sample randomization should be performed. When documenting the results of a trial, the appraiser should not have access to the results of the previous trials. A different data-collection sheet should be provided to each appraiser for each trial. Rather than a different data sheet, a data recorder may be used to “blind” the appraiser to the test data of previous runs.
• Gage R&R Study. This represents the analysis of the measurement variation. The measurement variation has two components:
- Repeatability, or precision under the same operating conditions (same appraiser/operator, test method, sample, etc.)
- Reproducibility, or the precision between appraisers when measuring the same sample with the same gage.
Typically, Minitab software is used to calculate % P/T for crossed-gage (non-destructive) tests. The raw data collected by appraisers, and all other required parameters and options, are entered into the Minitab, which then produces a standard report, with all associated statistics and graphs, titled “Gage R&R Study – ANOVA Method.”
In that gage R&R report, the “%Tolerance” column and the rows “Total Gage R&R, Repeatability and Reproducibility” contain the values needed for assessment against the acceptance criteria established in the protocol.
If the “%Tolerance” is greater than 30%, then gage R&R (TMV) has failed to meet the acceptance criteria set forth in the protocol. A thorough investigation is then needed to identify the root cause(s) of the failure and to determine remediation action(s). After the remediation is implemented, either an appropriate portion of the TMV or the entire TMV must be repeated.
Step 3: Prepare the TMV Report
The TMV report is a formal document written at the conclusion of the test method validation. Although every company has its own procedures and templates for TMVs, a basic TMV report includes the following items:
• Cover page with document title, document number, document version, and project number
• Executive summary – a summary of results, conclusions, issues, and resolutions
• Reference documents, including references to any related document numbers and versions
• Deviations to protocol, if applicable, including an explanation of acceptance criteria
• Results of the validation, including:
- Data summary
- Explanation of any excessive variation, investigations completed, conclusions, and/or corrective actions taken
- Uncovered errors and how they were resolved
- Any new sources of test method variation that were identified and how they could be minimized
- Revisions to the test method, if needed
• Conclusion stating whether the test method met or did not meet its intended purpose
Step 4: Document the TMV Activities
Once the TMV is completed, ensure that all documentation associated with the TMV is error free, has been released through the formal approval process, and is filed in the design history file (DHF), with the manufacturing documentation, or in any other appropriate database, as the case may be. Ensure that everything fully complies with the company’s procedures and policies as well as industry regulations and standards.